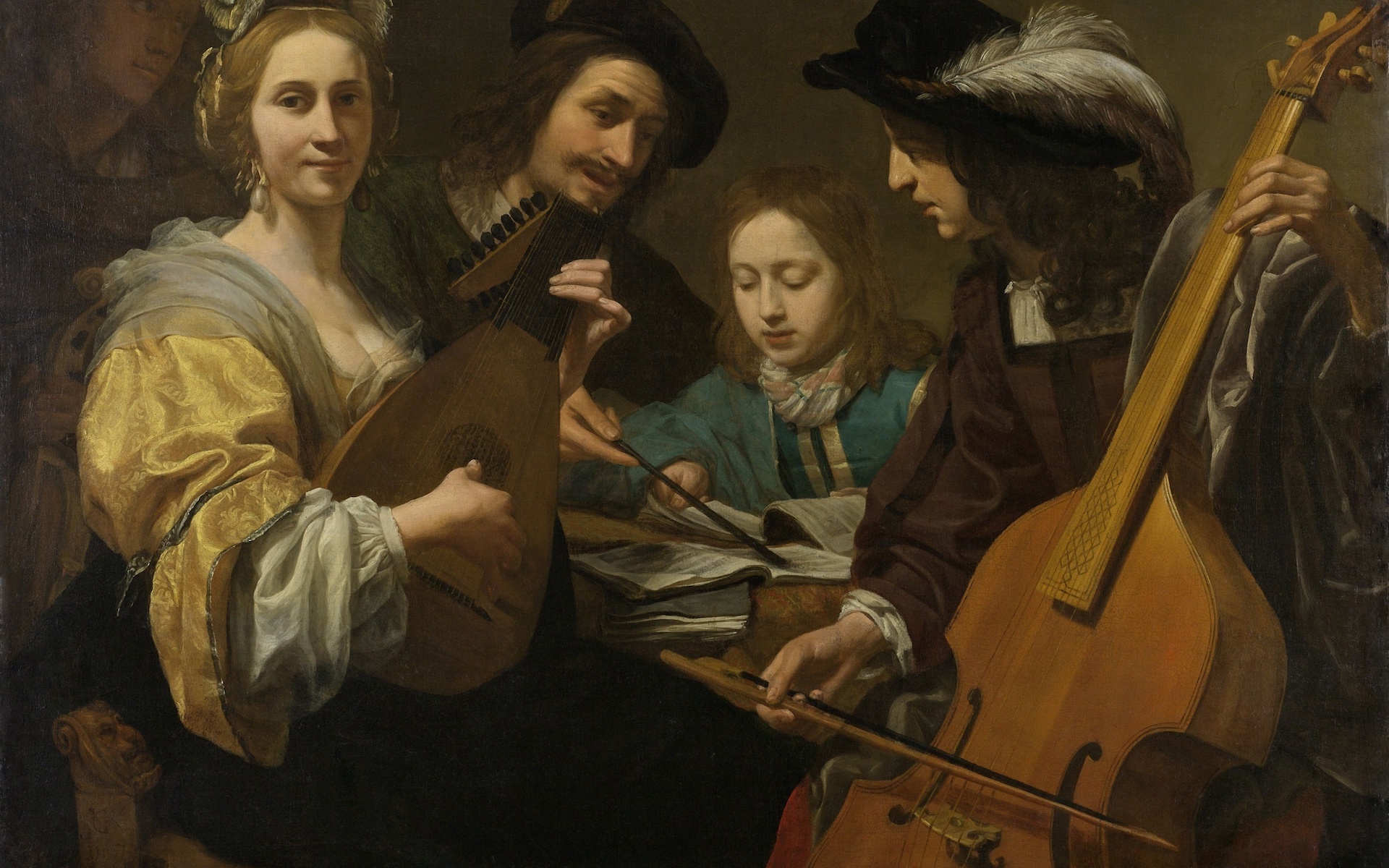
What is Music History?
Definition and Scope
Music history is the study of how music has evolved over time, shaped by cultural, societal, and technological changes. It encompasses the study of musical styles, genres, composers, and the development of musical instruments and notation. From ancient rituals to modern-day streaming, music has always been integral to human culture and history.
The Role of Music in Society
Throughout history, music has been a reflection of societal values, struggles, and triumphs. It has served as a tool for communication, expression, and celebration, often helping communities come together. Music has played a vital role in religious ceremonies, state functions, entertainment, and education. In many ways, cast-a-blast .com/ mirrors human history itself.
Ancient Music
The Origins of Music
Music likely began with the earliest humans using their voices, simple percussion, and natural objects as instruments. Some anthropologists suggest that music predates spoken language, being a form of communication and ritual. The exact origins of music are lost in time, but it’s believed to have served as both a spiritual and social tool.
Music in Ancient Civilizations
Ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians, Greeks, Romans, and Chinese, all had music deeply embedded in their culture. The Egyptians used music in religious rituals, while Greek philosophers like Pythagoras and Plato studied the mathematical properties of music. The Greeks are credited with the development of musical scales and the study of harmony, which would become crucial to Western music.
Medieval Music (500-1400)
Early Medieval Music
Medieval music was primarily religious, with early Christian music dominated by Gregorian Chant. These chants were monophonic, meaning they had a single melodic line with no harmony. Music was seen as a divine activity, and it was mainly performed in churches and monasteries.
Gregorian Chant and Its Influence
Gregorian Chant, named after Pope Gregory I, had a profound impact on the development of Western music. These chants were sung in Latin and were considered the purest form of religious music. Over time, polyphony (multiple independent voices) began to emerge, leading to more complex forms of music.
Development of Notation
Around the 9th century, music notation was developed, allowing music to be written down for the first time. This allowed compositions to be preserved and shared more widely, marking the beginning of more structured musical education and composition.
Renaissance Music (1400-1600)
The Rise of Polyphony
During the Renaissance, music became more complex. Polyphony, or the use of multiple independent voices, became a dominant feature of music, especially in choral works. Composers like Josquin des Prez and Palestrina refined polyphonic techniques, giving rise to a golden age of choral music.
Instrumental Music in the Renaissance
While vocal music remained dominant, the Renaissance also saw the development of instrumental music. New instruments, such as the lute and early keyboard instruments like the harpsichord, became more prominent. This period also saw the rise of instrumental ensembles and the precursor to modern orchestras.
Baroque Music (1600-1750)
Characteristics of Baroque Music
Baroque music is known for its ornate style, emotional expressiveness, and the use of contrast. Composers like Bach, Handel, and Vivaldi embraced the use of basso continuo (a continuous bass line) and elaborate ornamentation. The music was dramatic, often designed to evoke specific emotions in the listener.
Famous Baroque Composers
Some of the most famous composers from the Baroque period include Johann Sebastian Bach, who revolutionized music with his intricate counterpoint; George Frideric Handel, known for his operas and oratorios; and Antonio Vivaldi, famous for “The Four Seasons.”
Classical Music (1750-1830)
The Symphony and Sonata Forms
The Classical period marked a shift toward clarity, balance, and structure. Music moved away from the complexity of the Baroque and embraced forms like the symphony and sonata. Composers like Haydn, Mozart, and Beethoven crafted works with clear melodies, structured forms, and harmonic progressions.
Notable Classical Composers
Haydn and Mozart are considered the pillars of Classical music, each contributing significantly to the development of the symphony and opera. Beethoven bridged the Classical and Romantic periods, known for his bold and emotional works.
Romantic Music (1830-1900)
Emotion and Expression in Music
The Romantic era was all about emotion, individualism, and artistic freedom. Composers embraced intense emotion in their works, with pieces often evoking feelings of love, loss, or national pride. The music grew larger in scale, with orchestras becoming more expansive.
Influence of Nationalism
Nationalism became a significant influence in Romantic music, with composers using folk melodies and national themes to express their cultural pride. Composers like Chopin, Tchaikovsky, and Verdi infused their works with the sounds and rhythms of their native countries.
20th Century Music
Rise of Modernism and Experimental Music
The 20th century saw a dramatic shift in musical styles. Composers began experimenting with dissonance, atonality, and unconventional structures. Innovations like electronic music, jazz, and minimalism challenged traditional forms. Artists like Stravinsky, Schoenberg, and John Cage pushed the boundaries of what music could be.
The Birth of Popular Music
The 20th century also marked the rise of popular music genres like jazz, rock, and pop. The advent of recorded sound and radio made music more accessible to the masses, leading to the rise of superstars like Elvis Presley, The Beatles, and Michael Jackson.
Contemporary Music (2000-Present)
Digital Revolution in Music
The 21st century has seen the digital revolution completely change the music industry. Streaming services, digital production tools, and social media platforms have made it easier than ever to discover, produce, and share music. Genres continue to evolve, blending traditional and modern influences.
Genres and Trends in Modern Music
Today, music is more diverse than ever, with genres constantly fusing and evolving. From hip-hop and EDM to indie rock and global fusion, the landscape of contemporary music is vast and ever-changing. Technology has played a central role in this transformation, enabling artists to reach global audiences without traditional record labels.
Conclusion
The history of music is a fascinating journey that reflects the evolution of human culture and society. From ancient chants to modern-day electronic beats, music has always been a powerful means of expression, communication, and connection. As technology continues to shape the future of music, we can only imagine the new forms of creativity and innovation that will emerge.